What is an aneurysm?
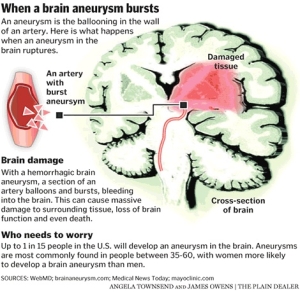 A brain aneurysm is a weak bulging spot on the wall of a brain artery much like a thin balloon or a weak spot on an inner tube. As the artery has thinned, the pounding of the blood flow through the artery weakens the artery. The blood flow causes the weakened artery wall to swell outward. This is very painful for the individual. This extreme pressure on the weakened artery may cause the aneurysm to rupture and allow blood to escape into the brain. This is a very serious condition that will require advanced surgical treatment, a coil or a clip. If the procedure is successful, the healing and recovery can begin.
A brain aneurysm is a weak bulging spot on the wall of a brain artery much like a thin balloon or a weak spot on an inner tube. As the artery has thinned, the pounding of the blood flow through the artery weakens the artery. The blood flow causes the weakened artery wall to swell outward. This is very painful for the individual. This extreme pressure on the weakened artery may cause the aneurysm to rupture and allow blood to escape into the brain. This is a very serious condition that will require advanced surgical treatment, a coil or a clip. If the procedure is successful, the healing and recovery can begin.
Statistics and Facts:
- An estimated 6 million people in the US have an unruptured brain aneurysm, or 1 in 50
- Approximately 30,000 people in the US will suffer a ruptured brain aneurysm. 40% of those that rupture are fatal. Of those that do survive, 66% will suffer permanent neurological damage.
- Approximately 15% of patients with a ruptured aneurysm die before reaching a hospital. Most of the deaths are due to the rapid and massive brain injury from the initial bleeding that is not correctable by medical or surgical intervention.
- 4 out of 7 that have a rupture, will sustain permanent disabilities.
- Brain aneurysms usually occur in adults between the ages of 35-60. Most aneurysms develop after the age of 40 and the median age of occurrence is 50.
- Women, more than men, suffer brain aneurysms at a ratio of 3:2.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is one of the most feared causes of acute headaches in the emergency rooms. Among all visits to an emergency room for headaches, 1%-4% has a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Accurate early detection and diagnosis is critical. As these hemorrhage can be fatal, and will also result in devastating neurologic outcomes. Despite widespread neuroimaging availability, misdiagnosis or delays in diagnosis occurs in up to 25% of patients. Failure to do a scan or lumbar puncture, results in 73% of misdiagnosis. This makes SAH a low-frequency, high-risk disease.
- There are more than 500,000 deaths each year caused by ruptured brain aneurysms, half the victims are younger than 50 years old.
- 10-15% of patients diagnosed with a brain aneurysm will most likely have more than one.
RISK FACTORS
- SMOKING
- High blood pressure/hypertension
- Congenital resulting from inborn abnormality of an artery wall
- Family history of brain aneurysm
- Age over 40
- Tumors
- Drug use, especially cocaine
- Traumatic Brain Injury
WARNING SIGNS/RISK FACTORS
- Localized headache
- Dilated pupils
- Blurred or double vision
- Pain above/behind the eyes
- Weakness or numbness
- Difficulty speaking
Ruptured aneurysms usually result in a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) defined as bleeding into the brain. When blood escapes, it may cause sudden symptoms:
- Sudden/severe headache, worst headache of your life
- Loss of consciousness
- Nausea/vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Sudden blurred or double vision
- Sudden pain above or behind the eye
- Trouble walking or dizziness
- Sudden weakness or numbness
- Seizure
Seek Immediate medical assistance for any of the above symptoms.


